General information Like any other living organism, plants have a cellular structure, although they do not contain intercellular substance. The difference between their cells and others is their narrow specialization, which leads to a decrease in the ability to divide. In biology I distinguish
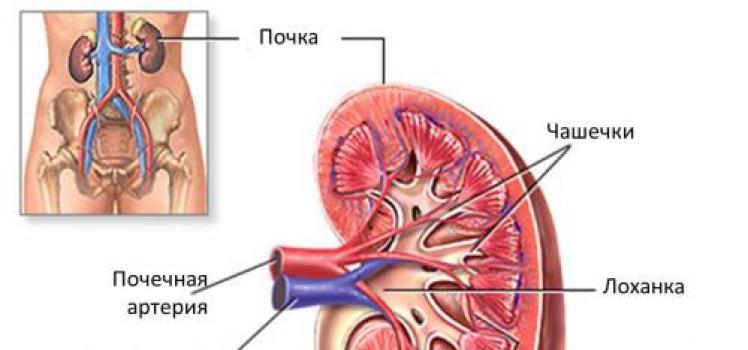
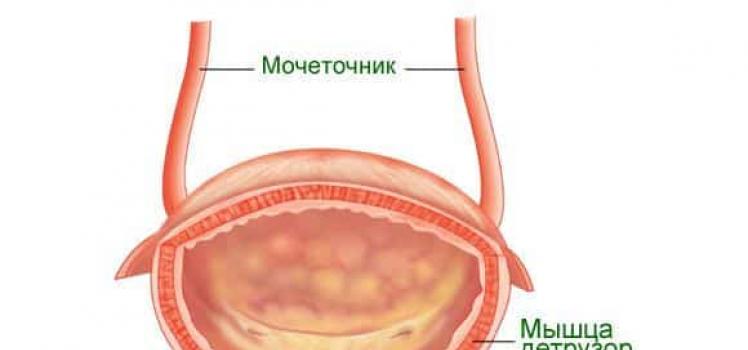
The human urinary system includes organs responsible for the formation, accumulation and removal of urine from the body. The system is designed to cleanse the body of toxins and hazardous substances while maintaining the required water-salt balance. Consider
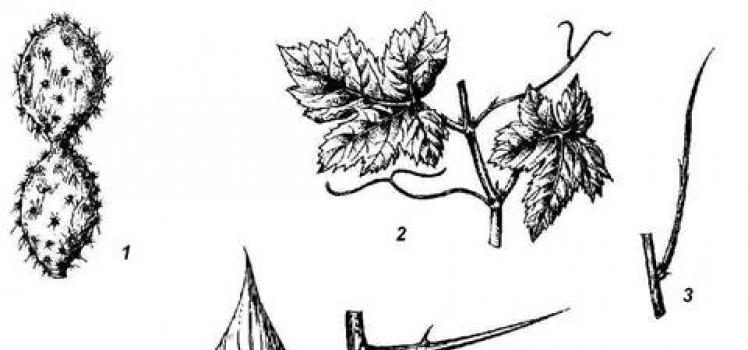
The shoot of a plant is one of the main vegetative organs. It consists of three parts: root, stem and leaf. In all existing higher plants they are homologous to each other and perform different functions. Phylogenesis of shoots In the context of historical
1. Kingdom of Mushrooms. 1.1. General characteristics. Mushrooms are a large group of organisms, numbering about 100 thousand species. They occupy a special position in the system of the organic world, apparently representing a special kingdom, along with the kingdoms of animals and plants.
The essence of this function comes down to the following process: in the event of damage to a medium or thin blood vessel (by squeezing or cutting the tissue) and external or internal bleeding occurs, a blood clot is formed at the site of destruction of the vessel.
The embryo is either from an axillary or accessory (adventitious) bud. Thus, the bud is a rudimentary shoot. When a seed germinates from the embryonic bud, the first shoot of the plant is formed - its main shoot, or shoot of the first order. From the main
The human body is a “full cycle factory”, continuously producing many substances, many of which are harmful and must be eliminated from the body. There are several ways to do this. All harmful substances are eliminated through breathing, sweat, feces and urine. So
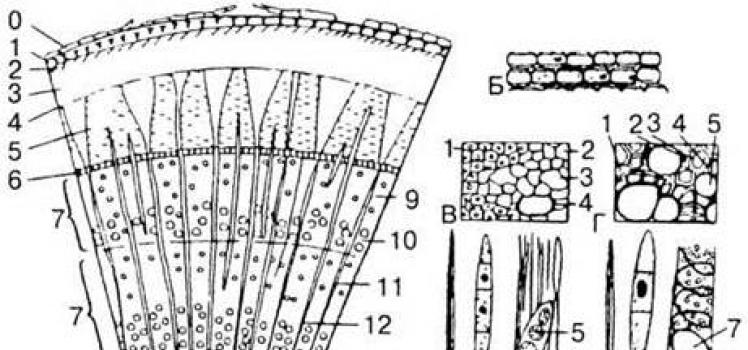
ESCAPE - VEGETATIVE ORGAN. ESCAPE SYSTEMS Parts of an escape. A shoot is a complex organ consisting of a stem, leaves, and buds (Fig. 5). The stem has nodes and internodes. A node is a section of the stem on which leaves and buds are located. The section of the stem between adjacent
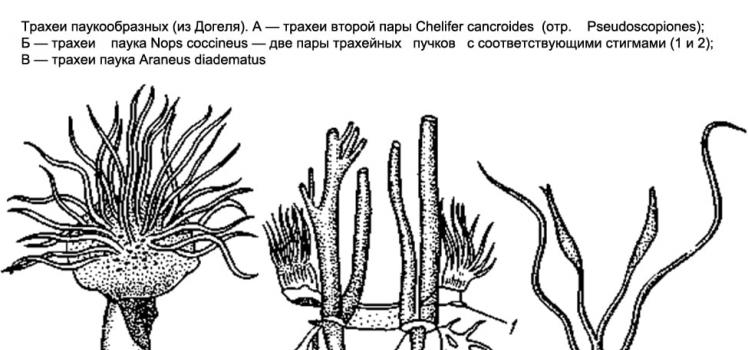
The class of arachnids unites over 36,000 species of terrestrial chelicerates, belonging to more than 10 orders. Arachnida are higher chelicerate arthropods with 6 pairs of cephalothorax limbs. They breathe through the lungs or trachea and have, in addition to coxals,
The shoot, like the root, is the main organ of the plant. Vegetative shoots typically perform the function of aerial nutrition, but have a number of other functions and are capable of various metamorphoses. Spore-bearing shoots (including the flower) are specialized to