Representatives of arachnids, class characteristics (photo)
The characteristic features of the structure of arachnids are associated with their adaptability to life on land. Representatives of the class belong to land arthropods with eight pairs of limbs.
Representatives of arachnids have a body consisting of two sections. At the same time, its connection can be represented either by a thin partition or by a tight bond. Antennae are absent in representatives of this class.
In the front part of the body are such limbs as mouth organs and walking legs. Arachnids breathe with the help of lungs and trachea. simple. Some species are completely absent.
The nervous system is represented by nerve nodes. The skin is hard, three-layered. There is a brain, consisting of anterior and posterior. represented by the heart in the form of a tube and an open circulatory system. Arachnids are dioecious individuals.
Ecology of arachnids
The first insects to adapt to life on land were precisely the representatives of arachnids. They can lead both diurnal and nocturnal active mode of existence.

Class overview
Zoologists conditionally subdivide the arachnid class into several orders. The main ones are scorpions, ticks, salpugs.
Scorpion Squad
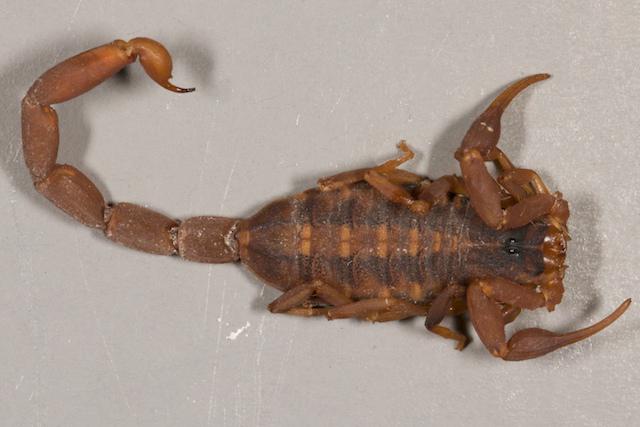
The scorpion is an atypical spider, which is why it is singled out in a separate detachment.
Spider-like representatives of the "scorpion" type are small in size, no more than 20 centimeters. His body consists of three well-defined sections. On the front there are two large eyes and up to five pairs of small lateral ones. The body of a scorpion ends with a tail in which a poisonous gland is located.
The body is covered with a thick and hard cover. A scorpion breathes with the help of lungs. They chose an area with a warm and hot climate as their habitat. At the same time, scorpions are divided into two subspecies: living in humid areas and in dry places. The attitude to air temperature is also ambiguous: there are subspecies that prefer a warm climate and high temperatures, but some tolerate cold very well.
Scorpions get food in the dark, they are distinguished by increased activity in the hot season. The scorpion discovers its prey by catching the oscillatory movements of a potential victim.

Scorpion breeding
If we talk about which arachnids are viviparous, then it is scorpions that for the most part bear offspring. However, there are also oviparous ones. The growth of embryos located in the body of the female is a rather slow process, and pregnancy can last more than a year.
Babies are born already in the shell, and after birth they immediately stick to the mother's body with the help of special suction cups. After about 10 days, the brood breaks away from the mother and begins to exist separately. The period of growing up in small individuals lasts about one and a half years.
The poisonous tail of a scorpion is an organ of attack and defense. True, the tail does not always save its owner from predators. Some animals know how to avoid blows, and then the predator itself becomes food. But if the scorpion nevertheless stung the victim, then many small invertebrates die almost immediately from the injection. Larger animals can live a day or two.
For a person, the aggression of a scorpion does not end in death, however, in modern medicine, cases with very serious consequences have been recorded. A swelling occurs at the site of the lesion, which can be quite painful, and the person himself becomes more lethargic and may experience attacks of tachycardia. After a couple of days, everything goes away, but in some cases, the symptoms persist for a longer period.
Children are more sensitive to the effects of scorpion venom. There have also been cases of death among children. In any case, you should immediately seek qualified help after
Solpuga Detachment
Recall that we are considering the class Arachnida. Representatives of this order are widely distributed in countries with a warm climate. For example, very often they can be found on the territory of the Crimea.
They differ from scorpions in a large dismemberment of the body. At the same time, the solid jaws of the salpuga perform the function of catching and killing the victim.
Salpugs do not have venom glands. Attacking a person, salpugs damage the skin with sharp jaws. Quite often, infection of the wound occurs simultaneously with the bite. The consequences are: inflammation of the skin at the site of injury, accompanied by pain.
This was a characteristic of arachnids, a salpuga detachment, and now consider the next detachment.

Spiders
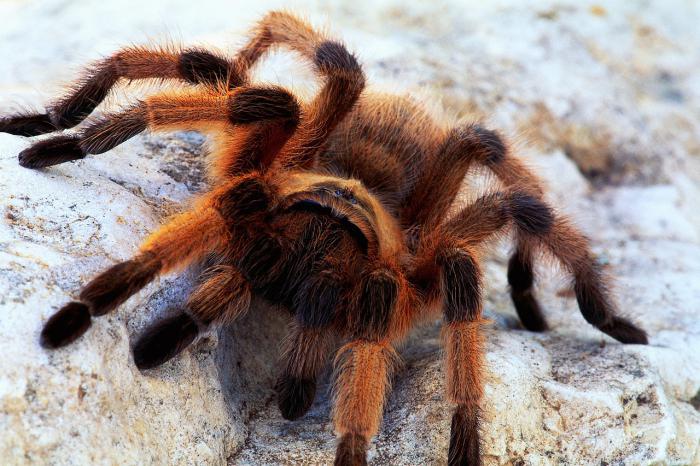
This is the most numerous order, numbering more than 20 thousand species.
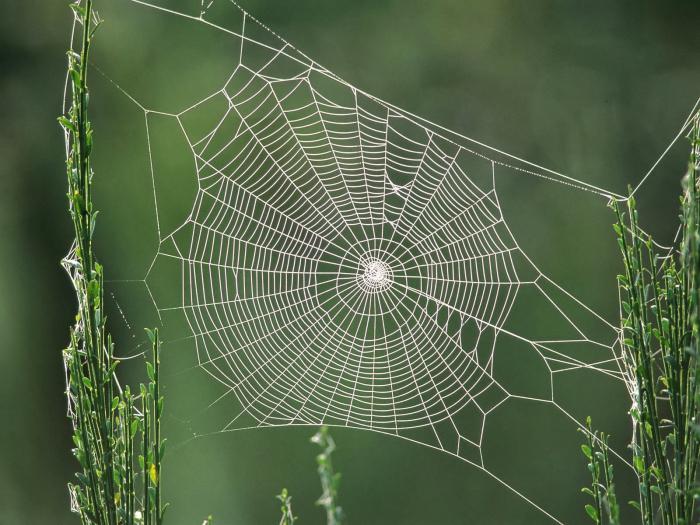
Representatives of different species differ from each other only in the form of the web. Ordinary house spiders, which can be found in almost any home, weave a web that resembles a funnel in shape. Poisonous representatives of the class create a web in the form of a rare hut.
Some spiders do not weave a web at all, but lie in wait for their prey, sitting on flowers. The color of insects in this case is adapted to the shade of the plant.
Also in nature, there are spiders that hunt for prey by simply jumping on it. There is another, special category of spiders. They never stay in one place, but constantly move in search of prey. They are called wolf spiders. But there are also ambush hunters, in particular, a tarantula.

Spider structure
The body consists of two sections connected by a septum. In the front of the body are the eyes, under them are hard jaws, inside of which there is a special channel. It is through it that the poison from the glands enters the body of the caught insect.
The sense organs are the tentacles. The body of the spider is covered with a light, but durable cover, which, as it grows, is shed by the spider, in order to be replaced later by another.
On the abdomen are small growths-glands that produce cobwebs. Initially, the threads are liquid, but quickly become solid.
The spider's digestive system is quite unusual. Having caught the victim, he injects poison into it, with which he first kills. Then gastric juice enters the body of the victim, completely dissolving the insides of the caught insect. Later, the spider simply sucks out the resulting liquid, leaving only the shell.
Breathing is carried out with the help of the lungs and trachea, located in the front and back of the abdomen.
The circulatory system, like all representatives of arachnids, consists of a heart tube and an open circulation. The nervous system of a spider is represented by nerve nodes.
Spiders reproduce by internal fertilization. The females lay eggs. Subsequently, small spiders appear from them.

Squad Ticks
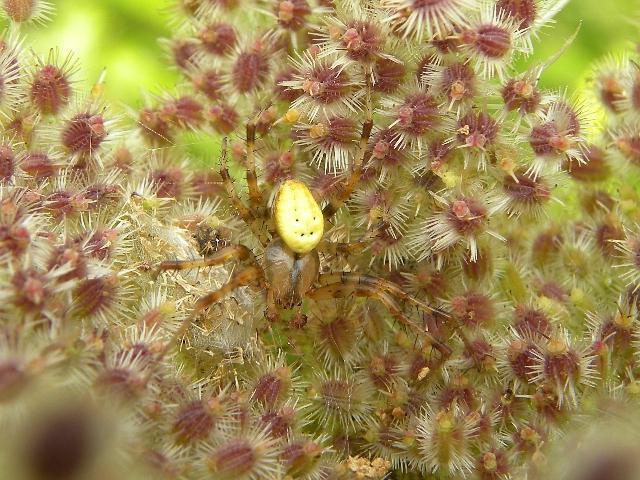
The order Ticks includes small and microscopic arachnids with an undivided body. All ticks have twelve limbs. These representatives of arachnids feed on both solid and liquid food. It all depends on the type.
The digestive system of ticks is branched. There are also organs of the excretory system. The nervous system is represented by the nerve chain and the brain.
The oral apparatus, like all representatives of the class, is located in front of the body and is represented by a proboscis and strong sharp teeth. With their help, the tick is held on the body of the victim until it is completely saturated.
This was a brief description of some representatives of the arachnid class.
We hope that the information will be useful to you.