Plant shoot: structure and function
The organs of flowering plants, the most evolutionarily developed representatives of this kingdom of wildlife, have a fairly diverse structure and functions. The underground part of the plant is called the root, the aboveground part is called the shoot. It is the shoot of plants that performs the most important functions: gas exchange, photosynthesis, transpiration, vegetative reproduction and its optimal location in relation to the sun.
Origin of the escape
In the process of evolution, this organ appears in the first land-dwellers - rhinophytes. Its stems were creeping and forked, because they were still poorly developed. But even with such a primitive structure, the photosynthetic surface increased, which means that the plant organism was better provided with carbohydrates.
in plants
A shoot is the aerial part of a plant, consisting of a stem and leaves. All of these organs are vegetative, providing growth, nutrition, and asexual reproduction.
The shoot of plants also contains rudimentary organs - the kidneys. There are two types of kidneys: vegetative and generative. The first type consists of a rudimentary stem and a leaf, on top of which there is a growing cone. If, in addition to the stem and leaves, the bud contains the beginnings of flowers or inflorescences, it is called generative. In appearance, such kidneys are distinguished by larger sizes and a rounded shape.
The place to which the leaf is attached on the stem is called the node, and the distance between the nodes is called the internode. The angle between the stem and the leaf is called the axil.
In the process of development, organs responsible for generative (sexual) reproduction also appear on the shoot: flower, fruit and seed.
Escape development from the kidney
With the onset of favorable conditions in spring, meristem cells begin to actively divide. Shortened internodes increase in size, resulting in a young shoot of plants. At the very top of the stem are the apical buds. They provide the growth of the plant in length. Axillary and adnexal buds are located in the leaf axil or internode, respectively. Due to them, the stem forms lateral shoots, i.e. branches.
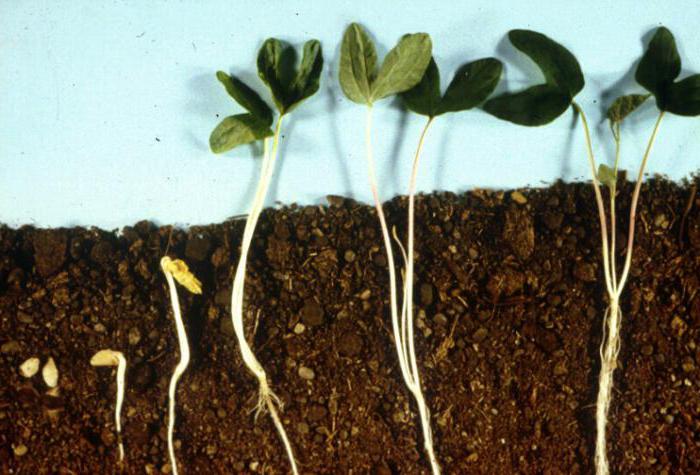

Plant branching methods
Depending on the structure, there are several ways of branching shoots:
- dichotomous. The most primitive type of branching, in which two grow from one point of growth, two from each of them, etc. This is how some algae and higher spore plants grow: club mosses and ferns.
- Primopodial. Such branching can be seen both in gymnosperms (pine, spruce) and (oak, maple). For a long time, the plants grew in length, followed by the formation of lateral branching.
- Sympodial. With this method, apical growth, on the contrary, stops. And the lateral buds are actively growing, forming more and more lateral shoots. Pear, cherry and other flowering plants are typical examples of this type of growth.
Shoot modifications
What is an escape in plants and how does it look, of course, everyone knows. But environmental conditions often require the appearance of additional functions. This is easily provided by the organs of flowering plants. The shoot is modified, acquiring new structural features, while it consists of parts of a standard shoot.
The main modifications of the escape include:
- Rhizome - located underground, where it most often grows horizontally. It has elongated internodes and buds, from which leaves appear on the surface of the earth in a favorable period. Therefore, plants with rhizomes (lily of the valley, wheatgrass, valerian) are very difficult to get rid of. After tearing off the leaves, the shoot itself remains in the ground, growing more and more.
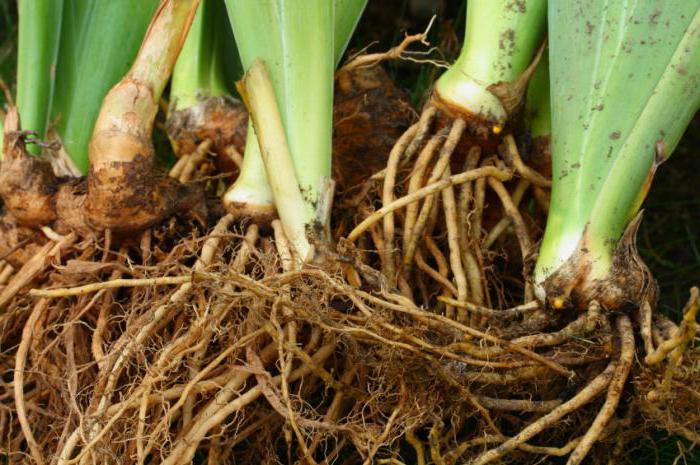

- The tuber is a thickened internode with buds - eyes. The most prominent representative of plants that form tubers is potatoes. Since it grows in the ground, it is often confused with a modified root. However, there are also above-ground tubers, for example, kohlrabi.
- Bulb - a modified shoot of plants with well-developed leaves located on a flat stem - the bottom. Typical for garlic, onion, tulip, lily. Nutrients accumulate in the inner succulent leaves, while the outer dry ones protect them from damage.
- Spines are a protective device of pear, sea buckthorn, hawthorn and other plants. Being in the axil of the leaf, they reliably protect the plant from animals that want to feast on them.
- Antennae are modified climbing shoots that fix plants in a certain position. Cucumber, grapes, pumpkin are the most common plants that use this device.
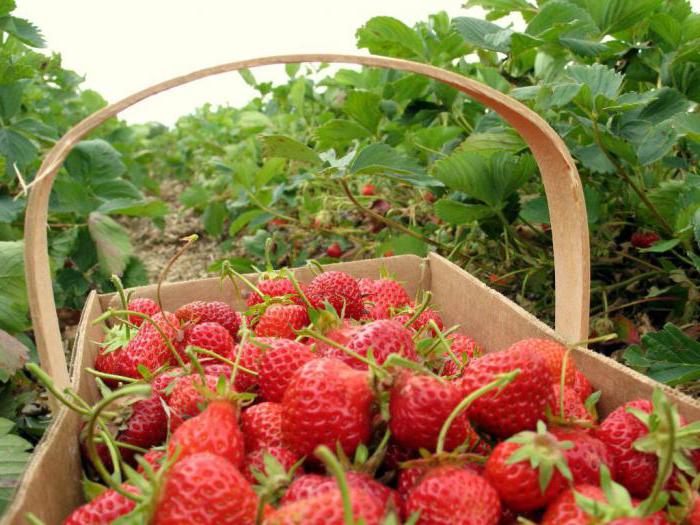

- Mustache - thin shoots with long internodes. Strawberries and wild strawberries reproduce vegetatively with the help of whiskers.
As you can see, the shoot of plants consists of parts that are functionally interconnected, can be modified depending on environmental conditions and give each plant its own unique look.