heat engine efficiency. Heat engine efficiency - definition formula
The operation of many types of machines is characterized by such an important indicator as the efficiency of a heat engine. Every year, engineers strive to create more advanced equipment, which, with less, would give the maximum result from its use.
Heat engine device
Before understanding what it is, it is necessary to understand how this mechanism works. Without knowing the principles of its action, it is impossible to find out the essence of this indicator. A heat engine is a device that does work by using internal energy. Any heat engine that turns into a mechanical one uses the thermal expansion of substances with increasing temperature. In solid-state engines, it is possible not only to change the volume of matter, but also the shape of the body. The operation of such an engine is subject to the laws of thermodynamics.
Operating principle
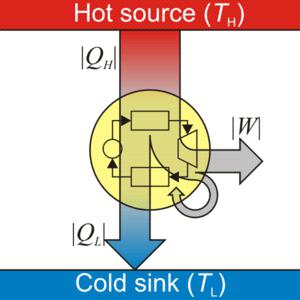
In order to understand how a heat engine works, it is necessary to consider the basics of its design. For the operation of the device, two bodies are needed: hot (heater) and cold (refrigerator, cooler). The principle of operation of heat engines (the efficiency of heat engines) depends on their type. Often, the steam condenser acts as a refrigerator, and any type of fuel that burns in the furnace acts as a heater. The efficiency of an ideal heat engine is found by the following formula:
Efficiency = (Theating - Tcold.) / Theating. x 100%.
At the same time, the efficiency of a real engine can never exceed the value obtained according to this formula. Also, this indicator will never exceed the above value. To increase the efficiency, most often increase the temperature of the heater and reduce the temperature of the refrigerator. Both of these processes will be limited by the actual operating conditions of the equipment.
During the operation of a heat engine, work is done, as the gas begins to lose energy and cools to a certain temperature. The latter is usually a few degrees above the surrounding atmosphere. This is the refrigerator temperature. Such a special device is designed for cooling with subsequent condensation of the exhaust steam. Where condensers are present, the temperature of the refrigerator is sometimes lower than the ambient temperature.
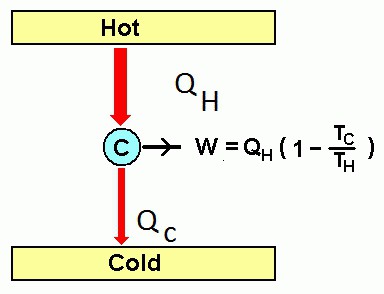
In a heat engine, the body, when heated and expanded, is not able to give all its internal energy to do work. Some of the heat will be transferred to the refrigerator along with or steam. This part of the thermal is inevitably lost. During the combustion of fuel, the working fluid receives a certain amount of heat Q 1 from the heater. At the same time, it still does work A, during which it transfers part of the thermal energy to the refrigerator: Q 2 Efficiency characterizes the efficiency of the engine in the field of energy conversion and transmission. This indicator is often measured as a percentage. Efficiency formula: η*A/Qx100%, where Q is the expended energy, A is useful work. Based on the law of conservation of energy, we can conclude that the efficiency will always be less than unity. In other words, there will never be more useful work than the energy expended on it. Engine efficiency is the ratio of useful work to the energy supplied by the heater. It can be represented as the following formula: η \u003d (Q 1 -Q 2) / Q 1, where Q 1 is the heat received from the heater, and Q 2 is given to the refrigerator. The work done by a heat engine is calculated by the following formula: A = |Q H | - |Q X |, where A is work, Q H is the amount of heat received from the heater, Q X is the amount of heat given to the cooler. |Q H | - |Q X |)/|Q H | = 1 - |Q X |/|Q H | It is equal to the ratio of the work done by the engine to the amount of heat received. Part of the thermal energy is lost during this transfer. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine is noted for the Carnot device. This is due to the fact that in this system it depends only on the absolute temperature of the heater (Тн) and cooler (Тх). The efficiency of a heat engine operating on is determined by the following formula: (Tn - Tx) / Tn = - Tx - Tn. The laws of thermodynamics made it possible to calculate the maximum efficiency that is possible. For the first time this indicator was calculated by the French scientist and engineer Sadi Carnot. He invented a heat engine that ran on ideal gas. It works on a cycle of 2 isotherms and 2 adiabats. The principle of its operation is quite simple: a heater contact is brought to the vessel with gas, as a result of which the working fluid expands isothermally. At the same time, it functions and receives a certain amount of heat. After the vessel is thermally insulated. Despite this, the gas continues to expand, but already adiabatically (without heat exchange with the environment). At this time, its temperature drops to the refrigerator. At this moment, the gas is in contact with the refrigerator, as a result of which it gives it a certain amount of heat during isometric compression. Then the vessel is again thermally insulated. In this case, the gas is adiabatically compressed to its original volume and state. Nowadays, there are many types of heat engines that operate on different principles and on different fuels. They all have their own efficiency. These include the following: An internal combustion engine (piston), which is a mechanism where part of the chemical energy of the burning fuel is converted into mechanical energy. Such devices can be gas and liquid. There are 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. They may have a continuous duty cycle. According to the method of preparing the fuel mixture, such engines are carburetor (with external mixture formation) and diesel (with internal). According to the types of energy converter, they are divided into piston, jet, turbine, combined. The efficiency of such machines does not exceed 0.5. Stirling engine - a device in which the working fluid is in a closed space. It is a kind of external combustion engine. The principle of its operation is based on periodic cooling/heating of the body with the production of energy due to a change in its volume. This is one of the most efficient engines. Turbine (rotary) engine with external combustion of fuel. Such installations are most often found in thermal power plants. Turbine (rotary) internal combustion engines are used at thermal power plants in peak mode. Not as common as others. A turboprop engine generates some of the thrust due to the propeller. The rest comes from exhaust gases. Its design is a rotary engine on the shaft of which a propeller is mounted. Rocket, turbojet and which receive thrust due to the return of exhaust gases. Solid state engines use a solid body as fuel. When working, it is not its volume that changes, but its shape. During operation of the equipment, an extremely small temperature difference is used. Is it possible to increase the efficiency of a heat engine? The answer must be sought in thermodynamics. It studies the mutual transformations of different types of energy. It has been established that it is impossible to convert all available thermal energy into electrical, mechanical, etc. At the same time, their conversion into thermal energy occurs without any restrictions. This is possible due to the fact that the nature of thermal energy is based on the disordered (chaotic) movement of particles. The more the body heats up, the faster the molecules that make it up will move. Particle motion will become even more erratic. Along with this, everyone knows that order can be easily turned into chaos, which is very difficult to order.Heat engine operation
Carnot engine
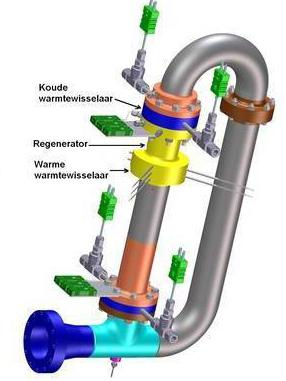
Varieties
Other types of heat engines
How can you increase efficiency