Internet data transmission channels
Data link - these are means of two-way data exchange, which include communication lines and equipment for transmitting (receiving) data. Data transmission channels connect information sources and information receivers.
Sample graphical depiction of links between Internet networks
Internet connection
As we have already said, computers permanently connected toInternetand traffic controllersonline information(permanent connection), called servers Internet .
The temporary connection of a computer to a network server is calledswitched connection. If this connection is made remotely (using telephone lines), then the connection is calledremote access connection.
To connect toInternet, you need to connect your computer to another computer that has a permanentIP-address. Each network server has a permanentIP - a d pec - this is internet protocol (InternetProtocol, IP) responsible for addressing.
In addition to havingIP-addressesconnection requires a modem. It must be connected to a computer for a dial-up connection to the ISP's server. Modems provide transmission of digital computer data via analog telephone channels at speeds up to 56 Kbps.
The remote access connection can be clearly seen in the figure
digital signal
digital signal
Telephone line (analog signal)
You also need to buy time from the Internet(orservice provider) . Organizations granting the right to such connection are called service providers.Internet. Usually these organizations are commercial and provide connection services under a contract.Internet Service Providers (ISPs) provide telephone lines that you must call to access the Internet.
When concluding a service contract, the provider provides the following information.
1. Phone number, according to whichdial-up connection using a telephone line and a modem.
2. Username ( login), which must be entered for registration at the time of connection.
3. Password ( password), entering which confirms the username.
Internet providers have high-speed connections of their servers to the Internet (1 Mbps and higher) and therefore can provide Internet access via telephone channels to hundreds and thousands of users at the same time. It is important that the phone number remains free. Regular and ADSL modems connect to the computer's USB port and to the telephone jack.
 ADSL modem example
ADSL modem example
 An example of a regular modem
An example of a regular modem
Many providers provide an electronic mailbox as an additional service, and you can receive messages from anywhere on our planet. If this organization is scientific or educational, it can provide its employees and partners with a free connection, but at the same time control the nature of their work on the Web.
Large organizations connect their local networks to the Internet on an ongoing basis, and become part of the Internet themselves.
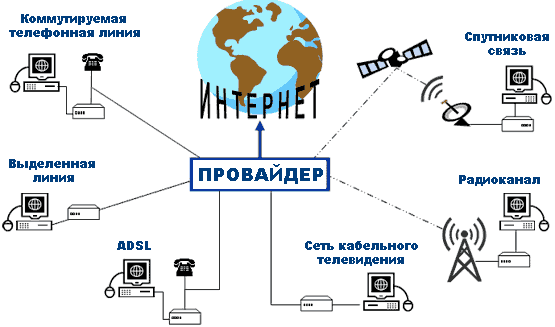
There are a lot of ways to connect to the provider's equipment. This is a connection via dial-up telephone line, leased line, digital telephone connection, cable television network, satellite channels, radio channel.
Data channels
Depending on the physical medium of data transmission, communication channels can be divided into:
wire communication lines without insulating and shielding braids;
cable, where such communication lines as twisted pair cables, coaxial cables or fiber optic cables are used for signal transmission;
wireless (radio channels of terrestrial and satellite communications), using electromagnetic waves that propagate through the air to transmit signals.
Wired communication lines
Wired (overhead) communication lines are used to transmit telephone and telegraph signals, as well as to transmit computer data. These communication lines are used as trunk communication lines.
Wired communication lines can be used to organize analog and digital data transmission channels. The transmission speed over wired lines is very low. In addition, the disadvantages of these lines include noise immunity and the possibility of a simple unauthorized connection to the network.
Cable communication channels
There are three types of cables used in computer networks.
Twisted pair
The cable is used for data transmission at 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps.Coaxial cable
Bandwidth - 50-100 Mbps. The permissible length of the communication line is several kilometers.
Fiber optic cable (fiber optic)
Data transfer rate 3Gbps.
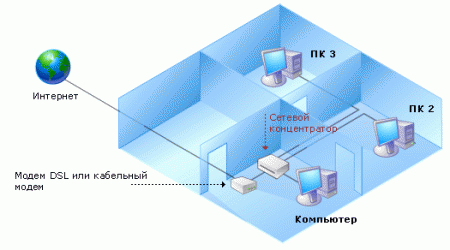
Wireless (terrestrial and satellite radio channels)
They are used in cases of connecting inconveniently located or remote computer networks, when cable laying is difficult or impossible.
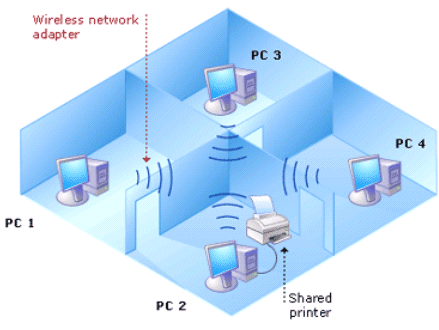
radio channels
Radio relay communication channels consist of a sequence of stations that are repeaters. Communication is carried out within the line of sight, the range between neighboring stations is up to 50 km. Digital radio relay lines (CRRS) are used as regional and local communication and data transmission systems, as well as for communication between cellular base stations.
satellite channel
Satellite systems use antennas to receive radio signals from ground stations and relay those signals back to ground stations. Satellite networks use three main types of satellites, which are in geostationary orbits, medium or low orbits. Satellites are launched, as a rule, in groups. Separated from each other, they can provide coverage of almost the entire surface of the Earth. The operation of the satellite data transmission channel is shown in the figure
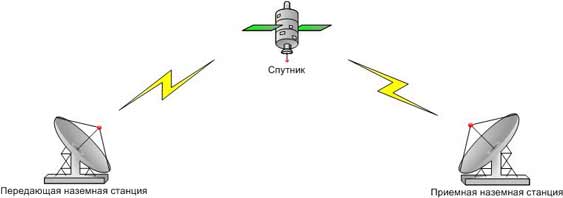
It is more expedient to use satellite communications to organize a communication channel between stations located at very large distances, and the possibility of servicing subscribers in the most inaccessible points. The throughput is high - several tens of Mbps.
Cellular communication channels
Cellular radio channels are built on the same principles as cellular telephone networks. Cellular communication is a wireless telecommunication system consisting of a network of ground base transceiver stations and a cellular switch (or mobile switching center).
Internet access technologies
WiFi
Notebook users can connect to the Internet using Wi-Fi wireless technology. At stations, airports and other public places, wireless access points connected to the Internet are installed. Within a radius of 100 meters, a laptop equipped with a wireless network card automatically accesses the Internet at speeds up to 54 Mbps.
PLC
PLC is a new telecommunications technology based on the use of power networks for high-speed information exchange (Internet from a socket). Allows you to transfer data over high-voltage power lines, without additional communication lines. The computer connects to the electrical network and accesses the Internet through the same outlet. No additional cables are required to connect to your home network. Various equipment can be connected to the home network: computers, telephones, burglar alarms, refrigerators, etc. In this technology, based on frequency division of the signal, a high-speed data stream is divided into several low-speed ones, each of which is transmitted on a separate frequency, followed by their combined into one signal. At the same time, Internet devices can “see” and decode information.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a technology for transmitting data over short distances (less than 10 m). The data transfer rate does not exceed 1 Mbps.
WiMAX
WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access), similar to WiFi - broadband Internet access technology. WiMAX, unlike traditional radio access technologies, also works on the reflected signal, outside the line of sight of the base station. Information can be transmitted over distances up to 50 km at speeds up to 70 Mbps.
WiMAX partially satisfies the conditions of 4G networks based on packet data transfer protocols. The 4G family includes technologies that allow data to be transmitted over cellular networks at speeds above 100 Mbps. and improved voice quality. VoIP technology is provided for voice transmission in 4G.
Radio Ethernet
Radio Ethernet - technology of broadband access to the Internet, provides a data transfer rate from 1 to 11 Mbps, which is shared among all active users. For the operation of the RadioEthernet channel, direct visibility between the antennas of the subscriber points is required. Radiusactionsbefore 30 km.
MMDS (Multichannel Multipoint Distribution System)
MMDS (Multichannel Multipoint Distribution System).These systems are capable of serving an area within a radius of 50-60 km, while the direct visibility of the operator's transmitter is not necessary. The average guaranteed data rate is 500 Kbps - 1 Mbps, but it is possible to provide up to 56 Mbps per channel.
Mobile GPRS - Internet
Mobile GPRS - Internet. To use the "Mobile Internet" service using GPRS technology, you must have a telephone with a built-in GPRS modem and a computer. GPRS technology provides data transfer rates up to 114 Kbps. When using GPRS technology, it is not the time of connection with the Internet that is charged, but the total amount of transmitted and received information. You will be able to view HTML pages, download files, work with e-mail and any other Internet resources.
Mobile CDMA-Internet
MobileCDMA-Internet.The CDMA standard network is fixed and mobile communications, as well as high-speed mobile Internet. To use the "Mobile Internet" service using CDMA technology, you must have a telephone with a built-in CDMA modem or CDMA modem and a computer. CDMA technology provides data transfer rates up to 153 Kbps or up to 2400 Kbps - using EV-DO Revision 0 technology.
Currently, CDMA technology provides third-generation mobile communication services. 3G mobile communication technologies (third generation - third generation) - a set of services that provides both high-speed mobile access to the Internet, and organizes videotelephony and mobile television. Mobile communication of the third generation is built on the basis of packet data transmission. Third-generation 3G networks operate in the 2 GHz band, transmitting data at speeds up to 14 Mbps.
Conclusion: each method of connecting to the network depends on several indicators, namely, on the financial situation, locality and on the needs of consuming Internet resources.