Germany - Learning is not boring!
Capital:East Berlin
Largest cities: East Berlin, Dresden, Leipzig
Language: German
Currency unit: GDR stamp
Area : 108333km 2
Population: 16675 million people
Form of government :one-party socialist republic
The German Democratic Republic (GDR, East Germany) is a now defunct socialist state located in Central Europe, founded on October 7, 1949 in the Soviet occupation zone of Germany and the eastern sector of Berlin. The republic officially ceased to exist and was merged with GermanyOctober 3, 1990.
Timeline of GDR dates
Creation of the GDR
The world-historic victory of the anti-Hitler coalition, the main force of which was the Soviet Union, over German fascism in the Second World War of 1939-45 created the preconditions for the democratization of social and political life in Germany. These prerequisites were fully implemented on the territory of the future GDR. However, one very important mistake was made here, which later became one of the reasons for the disappearance of the GDR - the unification of the SPD and the KPD. Under the leadership of the SED, the working class, in alliance with other sections of the working people, with the full support and assistance of the Soviet military administration, which consistently carried out the decisions of the Potsdam Conference, carried out profound revolutionary transformations, rooted out fascism and militarism, and established an anti-fascist-democratic order.War criminals and active Nazis were removed from their posts and brought to justice. The National Socialist Party and its organizations were disbanded (whereas in the FRG most of the high-ranking Nazis retained their posts). About 9.3 thousand industrial enterprises belonging to monopolies, Nazis and war criminals were confiscated and transferred to the ownership of the people. Almost all railway transport was nationalized, people's banks were created instead of capitalist ones, as well as state and cooperative institutions. The people's sector emerged in the economy. In agriculture, an agrarian reform was carried out, which eliminated the landowner-Junker landownership. Local self-government bodies confiscated 13.7 thousand farms with a total area of 3.3 million hectares, transferring 2.2 million hectares to landless and land-poor peasants. On the rest of the confiscated lands, people's estates were created.
The ruling circles of the Western powers, together with the West German big bourgeoisie, which was supported by the right-wing leaders of the Social Democracy, in violation of the decisions of the Potsdam Conference, set a course for the revival of German militarism. The German monopolies and the Western occupation authorities stepped up their offensive against the democratic forces in the direction of a complete split of the country. Its completion was the formation in September 1949 of a separate West German state - the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG). On October 7, 1949, the working people of eastern Germany proclaimed the German Democratic Republic. The German People's Council (established in March 1948 by the German People's Congress) was transformed into a provisional People's Chamber; it put into effect the constitution of the GDR, the draft of which was discussed and approved by the people in 1948-49. On October 11, 1949, the provisional parliament elected V. Ilhelm Pick - a sincere communist, one of the founders of the Communist Party of Germany. On October 12, the Provisional Government of the GDR headed by O. Grotewohl was formed. The creation of the GDR was an important historical event in the life of the German people, a turning point in the history of Germany. The formation of the GDR was a natural result of the anti-fascist-democratic revolution, the response of the progressive forces of the German people to the split of Germany by the Western powers and the West German reaction. The GDR was the legitimate heir to the best historical traditions of the German people, the embodiment of the freedom-loving and socialist ideals of its best sons.
The Soviet government transferred to the GDR the control functions that belonged to the Soviet military administration. In 1949, the USSR, China, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Albania, DPRK and Mongolian People's Republic recognized the GDR by establishing diplomatic relations with it; Yugoslavia established diplomatic relations with the GDR in 1957, and Cuba in 1963.
Socialist transformations
The formation of the GDR was a decisive milestone in the process of the peaceful and gradual development of the anti-fascist-democratic revolution into a socialist one.
With the emergence of the GDR, along with the strengthening of the anti-fascist-democratic order, the process of creating the foundations of socialism began in it. Under the leadership of the SED, the working class, in alliance with the peasantry and other sections of the working people, carried out the transition from the anti-fascist-democratic state power to the worker-peasant power as a form of proletarian dictatorship, the 2nd conference of the SED (July 1952) proclaimed building the foundations of socialism the main task of the GDR. In building a new society, the GDR relied on the experience and comprehensive assistance of the USSR.
The GDR had to overcome difficulties associated primarily with the split of the country. The ruling circles of the FRG exercised the strongest political and economic pressure on the GDR, conducted subversive activities against it and organized numerous provocations. Also, the development of the country was hindered by a dangerous internal enemy - many former social democrats who ended up in the party as a result of the unification of the SPD and the KPD wanted only one thing - the speedy restoration of the bourgeois order in the country. It was they who played a decisive role in the destruction of the GDR.Measures were taken to improve the work of state bodies and to involve the broad masses of workers in government.

In an effort to ensure its state interests, as well as the security of other socialist countries and to stop the subversive activities carried out from West Berlin, the GDR, with the consent and approval of the Warsaw Pact states, carried out in August 1961 the necessary measures to strengthen security and control on the border with West Berlin . This had a beneficial effect on the entire further development of the GDR.In conditions of immediate danger to the GDR created by the remilitarization of the FRG, the working people of the GDR resolutely came out in favor of taking measures to defend the socialist gains. For this purpose, the National People's Army was formed in 1956..
The leadership of the GDR sought, despite the "Halstein Doctrine", through foreign policy activity to achieve international legal recognition of their state. It tried to overcome the diplomatic blockade set up by the FRG. That is why the SPD proposed the idea of a "new eastern policy"establishing, first of all, trade, economic and consular relations with developing countries.
Industry
The eastern regions of Germany, which became part of the GDR, were less industrially developed than the western ones, and suffered more during the war. In this regard, a whole number of industries had to be re-created in the GDR. The nationalization of large industrial enterprises made it possible to move to a planned economy. As a result of the implementation of the two-year (1949-1951) and five-year (1951-1955) plans, old industrial enterprises were restored and expanded, metallurgical plants were built based on raw materials imported from the USSR and other socialist countries.
In 1962, industrial production increased by 3.6 times compared with the production in these areas in 1936. In terms of industrial production, the GDR ranked fifth in Europe and tenth in the world. In terms of the rate of development, the GDR is ahead of the FRG. The main part of production (up to 90%) comes from the socialist sector of the economy. Over the years of its existence, the GDR has become a developed industrial state of the socialist type.
Among the socialist countries, the GDR is one of the largest suppliers of equipment, which goes primarily to the countries of Asia and Africa that have embarked on the path of independent development. According to the developed seven-year plan for the development of the economy (1959-1965), further development of heavy industry and an increase in the material and cultural standard of living of the working people are planned.
By 1961, it became clear that more and more people did not want to build a socialist bright future, border crossings became more frequent. The young people left, the future of the country. In July alone, about 200,000 people left the GDR across the border with West Berlin. ANDRThe leadership of the GDR, supported by the Warsaw Pact countries, decided to strengthen the country's state border with West Berlin.
August 13, 1961 on the recommendation of the meeting of the secretaries of the communist and workers' parties of the Warsaw Pact countriesand on the basis of the decision of the People's Chamber of the GDRwas erected Berlin Wall.
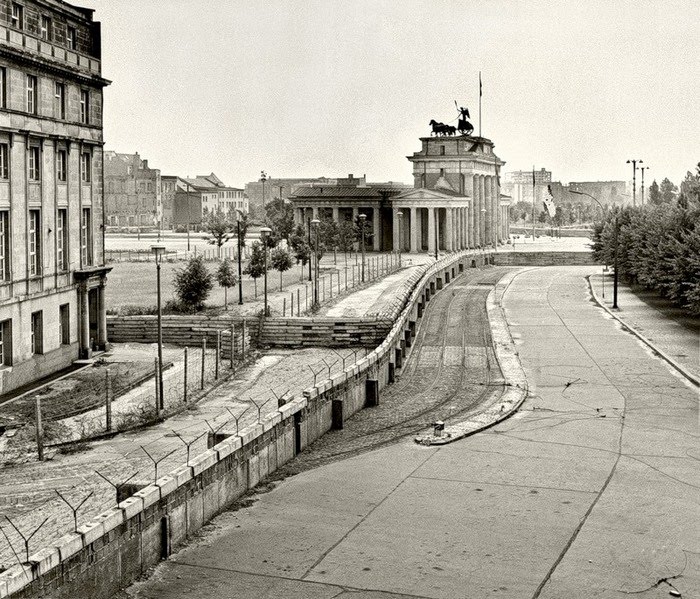 However, the construction of the rampart did not prevent further emigration from the territory of East Germany. People made their way through the rivers and dug. On average (before the construction of the fence), about half a million people traveled daily from the GDR to the FRG for various reasons. And in the twenty-eight years since the wall was built, only 5,075 successful illegal crossings have been made. For this, waterways, tunnels (145 meters underground), balloons and hang gliders, rams in the form of cars and bulldozers were used, they even moved along a rope between buildings.
However, the construction of the rampart did not prevent further emigration from the territory of East Germany. People made their way through the rivers and dug. On average (before the construction of the fence), about half a million people traveled daily from the GDR to the FRG for various reasons. And in the twenty-eight years since the wall was built, only 5,075 successful illegal crossings have been made. For this, waterways, tunnels (145 meters underground), balloons and hang gliders, rams in the form of cars and bulldozers were used, they even moved along a rope between buildings.
The following feature was interesting. People received free education in the socialist part of Germany, and began to work in Germany, because there were higher salaries.