Natural zones of the world: a brief description. Table "Natural zones of the world"
The warmth of the sun, clean air and water are the main criteria for life on Earth. Numerous climatic zones led to the division of the territory of all continents and water space into certain natural zones. Some of them, even separated by vast distances, are very similar, others are unique.
Natural areas of the world: what is it?
This definition should be understood as very large natural complexes (in other words, parts of the geographic belt of the Earth), which have similar, uniform climatic conditions. The main characteristic of natural zones is the flora and fauna that inhabits this territory. They are formed as a result of uneven distribution of moisture and heat on the planet.
Table "Natural zones of the world"
natural area | climate zone | Average temperature (winter/summer) |
Antarctic and Arctic deserts | Antarctic, arctic | 24-70°С /0-32°С |
Tundra and forest tundra | Subarctic and Subantarctic | 8-40°С/+8+16°С |
Moderate | 8-48°C /+8+24°C |
|
mixed forests | Moderate | 16-8°С /+16+24°С |
broadleaf forests | Moderate | 8+8°С /+16+24°С |
Steppes and forest-steppes | subtropical and temperate | 16+8 °С /+16+24°С |
temperate deserts and semi-deserts | Moderate | 8-24 °С /+20+24 °С |
hardwood forests | Subtropical | 8+16 °С/ +20+24 °С |
Tropical deserts and semi-deserts | Tropical | 8+16 °С/ +20+32 °С |
Savannahs and woodlands | 20+24°C and above |
|
Variable rainforests | subequatorial, tropical | 20+24°C and above |
Permanently wet forests | Equatorial | above +24°С |
This characteristic of the natural zones of the world is only introductory, because you can talk about each of them for a very long time, all the information will not fit in the framework of one table.
Natural zones of the temperate climate zone
1. Taiga. Surpasses all other natural zones of the world in terms of the area occupied on land (27% of the territory of all forests on the planet). It is characterized by very low winter temperatures. Deciduous trees do not withstand them, so the taiga is dense coniferous forests (mainly pine, spruce, fir, larch). Very large areas of the taiga in Canada and Russia are occupied by permafrost.
2. Mixed forests. Characteristic to a greater extent for the Northern Hemisphere of the Earth. It is a kind of border between the taiga and the broad-leaved forest. They are more resistant to cold and long winters. Tree species: oak, maple, poplar, linden, as well as mountain ash, alder, birch, pine, spruce. As the table "Natural areas of the world" shows, the soils in the zone of mixed forests are gray, not very fertile, but still suitable for growing plants.
3. Broad-leaved forests. They are not adapted to harsh winters and are deciduous. They occupy most of Western Europe, the south of the Far East, the north of China and Japan. Suitable for them is a maritime or temperate continental climate with hot summers and fairly warm winters. As the table "Natural zones of the world" shows, the temperature in them does not fall below -8 ° C even in the cold season. The soil is fertile, rich in humus. The following types of trees are characteristic: ash, chestnut, oak, hornbeam, beech, maple, elm. The forests are very rich in mammals (ungulates, rodents, predators), birds, including commercial ones.
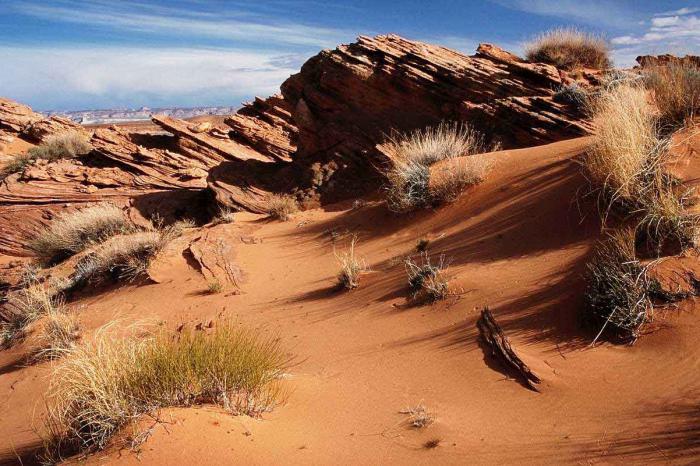

4. Temperate deserts and semi-deserts. Their main distinguishing feature is the almost complete absence of vegetation and sparse wildlife. There are a lot of natural areas of this nature, they are located mainly in the tropics. There are temperate deserts in Eurasia, and they are characterized by sharp temperature changes during the seasons. Animals are represented mainly by reptiles.
Arctic deserts and semi-deserts
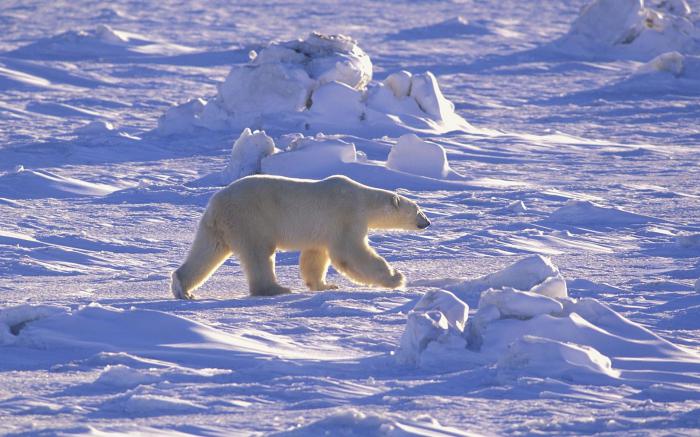
They are huge areas of land covered with snow and ice. The map of natural zones of the world clearly shows that they are located on the territory of North America, Antarctica, Greenland and the northern tip of the Eurasian continent. In fact, these are lifeless places, and polar bears, walruses and seals, arctic foxes and lemmings, penguins (in Antarctica) live only along the coast. Where the land is free of ice, lichens and mosses can be seen.

Moist equatorial forests
Their second name is rainforests. They are located mainly in South America, as well as in Africa, Australia and the Greater Sunda Islands. The main condition for their formation is a constant and very high humidity (more than 2000 mm of precipitation per year) and a hot climate (20 ° C and above). They are very rich in vegetation, the forest consists of several tiers and is an impenetrable, dense jungle that has become home to more than 2/3 of all types of creatures that now live on our planet. These rainforests are superior to all other natural areas of the world. Trees remain evergreen, changing foliage gradually and partially. Surprisingly, the soils of moist forests contain little humus.
Natural zones of the equatorial and subtropical climatic zone
1. Variably humid forests, they differ from rainforests in that precipitation falls there only during the rainy season, and during the period of drought that follows it, the trees are forced to shed their leaves. The animal and plant world is also very diverse and rich in species.
2. Savannas and woodlands. They appear where moisture, as a rule, is no longer enough for the growth of variable-humid forests. Their development occurs in the depths of the mainland, where tropical and equatorial air masses dominate, and the rainy season lasts less than six months. They occupy a significant part of the territory of subequatorial Africa, the interior of South America, partly Hindustan and Australia. More detailed information about the location is reflected in the map of natural areas of the world (photo).
hardwood forests
This climate zone is considered the most suitable for human habitation. Hardwood and evergreen forests are located along sea and ocean coasts. Precipitation is not so plentiful, but the leaves retain moisture due to the dense leathery shell (oaks, eucalyptus), which prevents them from falling off. In some trees and plants, they are modernized into thorns.
Steppes and forest-steppes
They are characterized by the almost complete absence of woody vegetation, this is due to the meager level of precipitation. But the soils are the most fertile (chernozems), and therefore are actively used by man for agriculture. Steppes occupy large areas in North America and Eurasia. The predominant number of inhabitants are reptiles, rodents and birds. Plants have adapted to the lack of moisture and most often manage to complete their life cycle in a short spring period, when the steppe is covered with a thick carpet of greenery.
Tundra and forest tundra
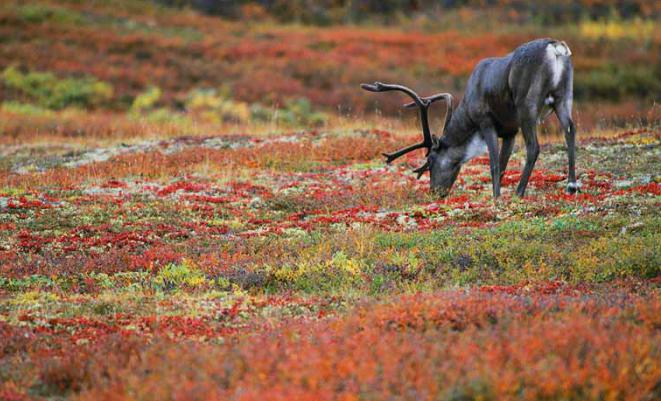

In this zone, the breath of the Arctic and Antarctic begins to be felt, the climate becomes more severe, and even coniferous trees cannot withstand it. Moisture is in excess, but there is no heat, which leads to swamping of very large areas. There are no trees at all in the tundra, the flora is mainly represented by mosses and lichens. It is believed that this is the most unstable and fragile ecosystem. Due to the active development of gas and oil fields, it is on the verge of an ecological disaster.
All natural areas of the world are very interesting, whether it is a desert that seems completely lifeless at first glance, boundless Arctic ice or thousand-year-old rain forests with boiling life inside.