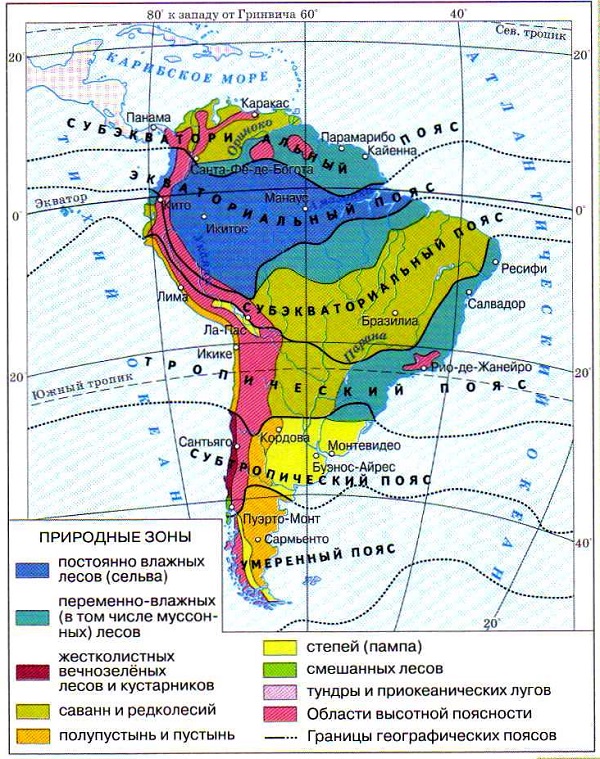
Natural areas of South America
South America is a continent with an amazing variety of flora and fauna. The natural zones of South America are uneven.
This is due to the strong difference in relief. The northern part of the continent is very different from the southern.
Geographic location of South America
The continent of South America is located in the Western Hemisphere. Its geographical location is fixed in tropical and equatorial latitudes. The Malvinas Islands in the shelf zone of the Atlantic Ocean and the islands of Tobago and Trinidad also belong to the continent.
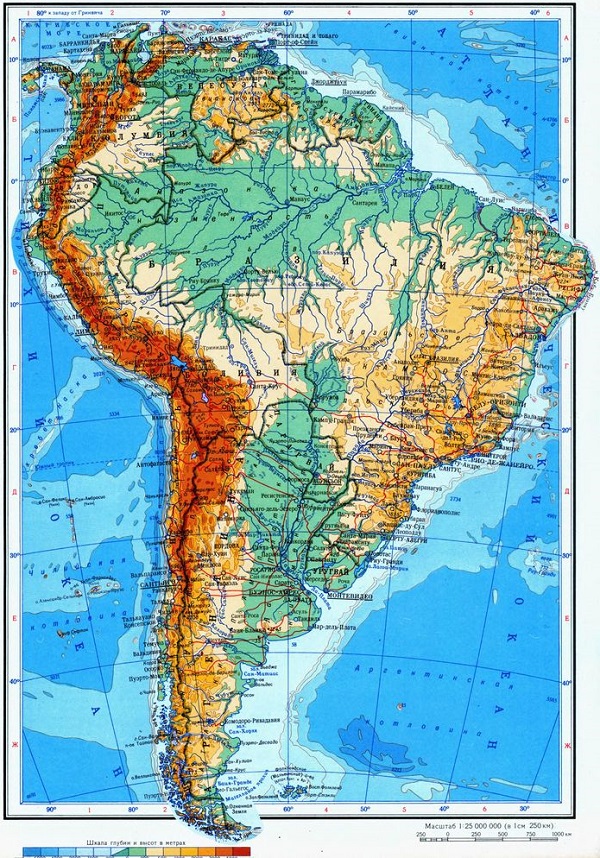
South America can be divided into two parts. The mountainous part is located in the west and represents the Andes belt. The eastern part is an ancient South American platform.
The Andes are among the most famous mountain ranges in the world. This is the longest and highest chain of mountains. Its length reaches 9 thousand kilometers. Mountain movement is still going on. Therefore, earthquakes and volcanic eruption very often occur in these places.
Characteristics of the natural zones of South America
Natural areas are unevenly located, as the continent has a very difficult terrain. South America differs from other continents in a huge variety of flora and fauna.
Due to its distance from the rest of the continents, South America has been able to preserve a huge number of animals and plants that cannot be found anywhere else in the world.

It is the birthplace of mahogany and chocolate trees, as well as potatoes, corn and tomatoes. Four species of kangaroos have been preserved here, you can meet armadillos, anteaters, and sloths. More than 300 species of birds live in South America, including the miniature hummingbird.

Most of the equatorial forests, which are considered to be the lungs of the planet, are located on this continent.
Amazonian selva
The equatorial forest of South America is called the Amazonian selva. They occupy large areas of the Amazonian lowland. These are very difficult places where you can find tree ferns, cinchona, ceiba.
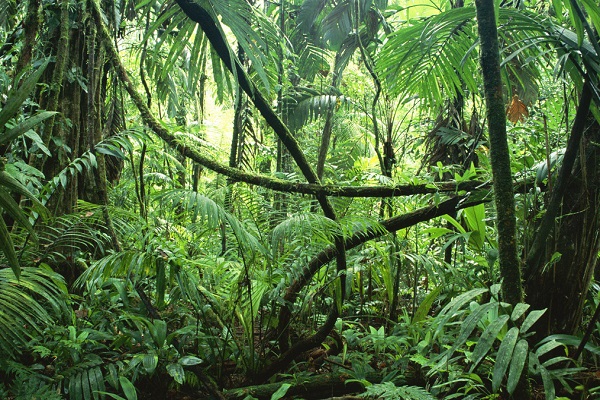

Tree trunks are tightly intertwined with vines. This forms a real wall that cannot be overcome.
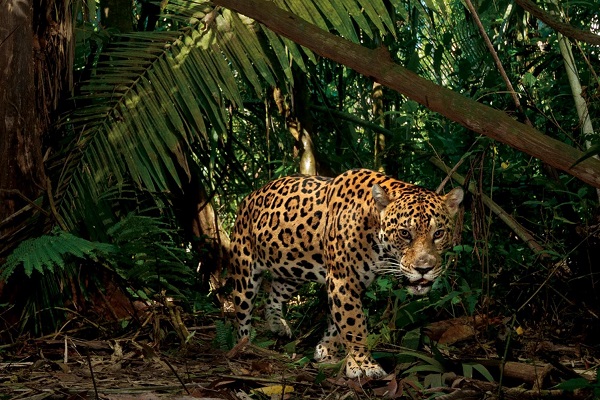

The forests are very rich in wildlife. Here you can meet howler monkeys, jaguars, colorful butterflies. The Amazon is home to a huge variety of fish species, huge anacondas, crocodiles.
Savannah
Savannahs are located in the subequatorial and tropical zones. They stretch in the Orinok lowland and are called llanos. There are deserted and wet savannahs.
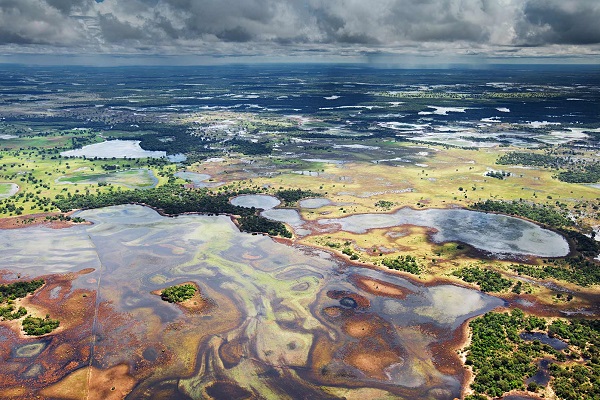

Llanos is flooded every year, the water stays there for about half a year, which turns these places into an impenetrable swamp. Mostly palm trees and sedge grow here.
In the savannahs of the Brazilian Plateau, low-growing shrubs grow. Among the vegetation, wax and oil palms are most common.
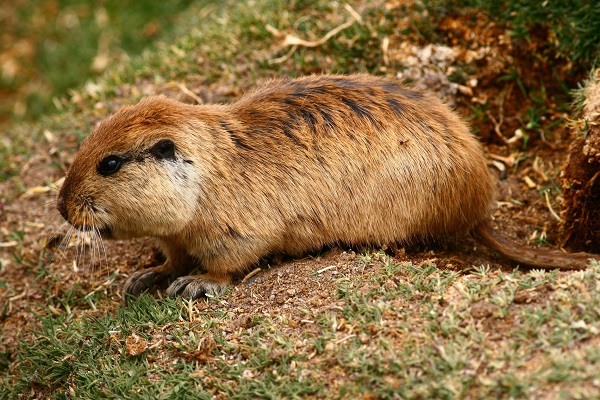

Savannah animals have a protective brown color. A huge number of rodents live here.
pampas
The position of the pampas zone is determined in the La Plata lowland. The land here is very fertile. These places are characterized by rich forbs.
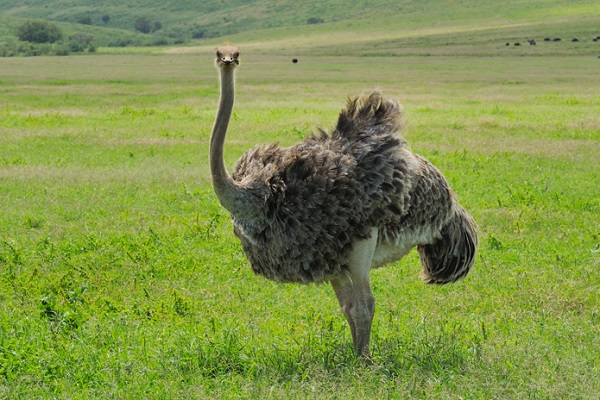

Local residents in these places are actively engaged in the cultivation of wheat and grass for livestock feed. The animal world is represented in great variety by rodents, you can meet the ostrich Nanda, puma, pampas deer and a cat.
desert
The desert zone is located in the tropical, subtropical and temperate climatic zones. This is one of the driest places on the planet, where precipitation may not fall for several years.

From the vegetation here you can find only dry cereals and cacti. The animal world is also scarce, represented by a spectacled bear, chinchilla, as well as the largest bird in the world - the Andean condor.
Coast
The coast of the Pacific Ocean is covered with hard-leaved evergreen forests. They consist of beeches, magnolias, Chilean cedar, larch. Of the animals, you can meet the otter, skunk, Magellanic dog, deer pudu.
Andes
Neighboring areas with evergreen forests are the Andes. Altitudinal zonality differs at different latitudes. The greatest number of mountains is located on the equator.
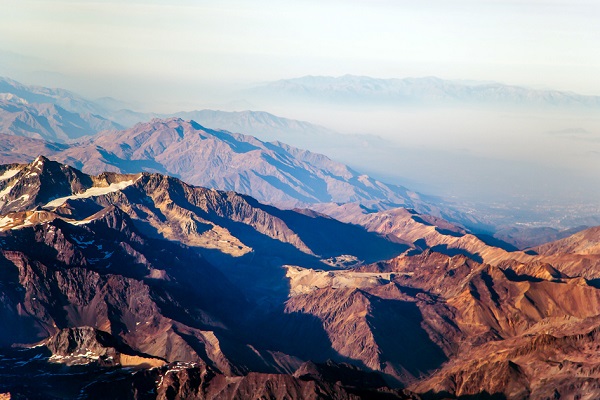

The Central Andes are characterized by a plateau, it is isolated from the influence of the ocean. Steppes and semi-deserts are located in these places.
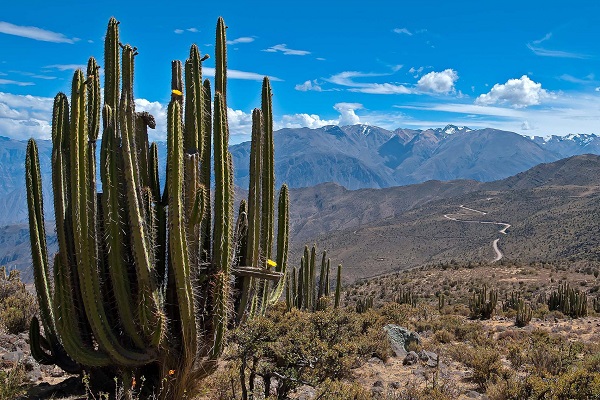

The world of animals and plants of the Andes differs depending on the altitude. At an altitude of 4500 meters, the zone of eternal glaciers and snow begins. Up to 3800 meters high mountain forest zone. Ferns and bananas grow at altitudes up to 2800.
Table of natural areas of South America
A plan for describing each natural zone of South America can be clearly seen in the table:
| Name of the natural area | Geographic location | Climate | Vegetable world | Animal world | Minerals | The soil |
| Selva | On both sides of the equatorial belt | Wet, hot | Chocolate, rubber trees | Hummingbirds, monkeys, sloths, toucans, porcupines | Gas, oil, aluminum | Wet, ferralitic |
| Savannah | Brazilian Highlands, Orinoco Lowland | subequatorial | Palm trees, bottle tree, mimosa, acacia | Deer, jaguars, baker pigs | Fertile in the Brazilian Highlands, dry elsewhere | Iron, tin, diamonds |
| pampas | La Plata lowland | Moderate | Feather grass, forbs | Rodents, llamas, ostriches, pampas cat | Chernozem | Uranus |
| desert | In the temperate zone | sharply continental | cacti, thorns | Rodents, armadillos | brown, infertile | Oil, gas, iodine, iron |
| Coast | Along the Pacific Coast | Wet | Mangroves, palm trees | Otter, skunk, pudu deer | Red-yellow ferralitic | Saltpeter |
| Andes | Equator region | Subtropical | Bamboo, softwood | Bears, llamas, chinchillas | Burozems | Oil Gas |
What natural areas are absent in South America
In South America, despite the variety of zones, there are no: mixed and deciduous forests, arctic desert,.
South America is divided into a large number of natural zones, which are very different from each other both in climate and in flora and fauna.
This continent is considered the wettest continent on earth, at the same time there are areas where precipitation does not fall for several years. South America is an amazing continent that contains a huge amount of unknown and unexplored.