African natural areas
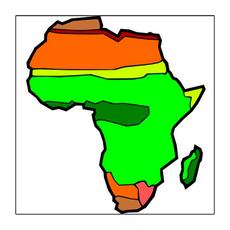
The black continent stands out in world geography in that the natural zones of Africa on the map are located almost correctly and symmetrically. This is due to the flat landscapes that are available almost everywhere on the mainland, as well as to the uniform position relative to the equator. Latitudinal zonality also depends on the amount of precipitation, which is uneven in these conditions.
However, in mountainous areas such a harmonious distribution is disturbed, the zones change with height. There are few such territories on the continent. Vegetation cover is also different in each zone, and this depends on the properties of the soil and climate conditions.
In the region of the equator, located in the center of Africa, there are equatorial forests (variably or permanently humid), the next natural zones extending north and south from the central area are savannahs, they are replaced by semi-deserts and deserts, but the mainland is framed by narrow strips of hard-leaved shrubs and forests (evergreen).
Map of natural areas of Africa
All the natural zones of Africa on the map are located in this order on the African mainland (from north to south):
Central equatorial characterized by numerous precipitations, there are also rich water resources - the Congo River, the Guinean coast. In addition, constant heat affected the formation of local vegetation.
Local soils have two shades - red and yellow, they are ferralitic, as the table of natural zones of Africa says, because due to chemical processes on the surface of the rocks, they have become enriched in aluminum and iron. Such soil is not fertile, because all the substances that appear in it quickly decompose, and then are washed out or absorbed by the flora.
The plants living here do an excellent job with the existing conditions:
- constant heat;
- high humidity;
- numerous rainfall.
For this they have:
- hard and dense leaves;
- supporting roots;
- several tiers.
The number of representatives of the flora is huge, many trees are distinguished by valuable wood, they also have edible fruits with good taste.
No less species and living beings:
- pigs;
- deer;
- okapi;
- gorillas;
- insects;
- invertebrates;
- microorganisms.

The following in the table of natural areas of Africa are variable wet forests, then comes the turn of the largest savannah, they are almost 40% of the entire mainland.
This zone is clearly different from the previous ones at first sight.
The amount of vegetation is related to rainfall and varies by region and season. When the rains are active, the grasses reach great heights, in places of drought the savannahs are covered with dead wood, bushes, there are rare trees (acacias most often).
It can almost be said for sure that it largely depends on this zone, because there are a huge number of national parks in the savannahs, as a unique variety of wild animals live here, attracting travelers from everywhere.
Meet here:
- giraffes;
- zebras;
- rhinos;
- elephants;
- hippos.
Of particular interest to visitors are predators:
- lions;
- hyenas;
- cheetahs;
- crocodiles.
The rich world of fauna includes many birds:
- ostriches;
- flamingos;
- storks;
- marabou;
- ibis.
In the districts semi-deserts savannahs are overgrown with thorny vegetation - herbs and shrubs, there are tree-like plants, euphorbia.
Considerable territories are allocated for desert, especially in the northern sub-region where there is the majestic Sahara. These lands are by no means lifeless, here, although rare, they are found:

Animals are just as adaptable.
- turtles;
- lizards;
- snakes;
- beetles;
- scorpions.
In different deserts throughout the mainland, there are certain representatives of flora and fauna, which depends on climatic and other conditions, each of them is unusual and multifaceted.
The most extreme natural zones of Africa on the map are characterized by the presence hard-leaved vegetation, they are in the very south or north, respectively. Here there are fertile brown soils that have formed under the following natural conditions of the Mediterranean climate:
- hot summer, dry;
- warm winter, wet.
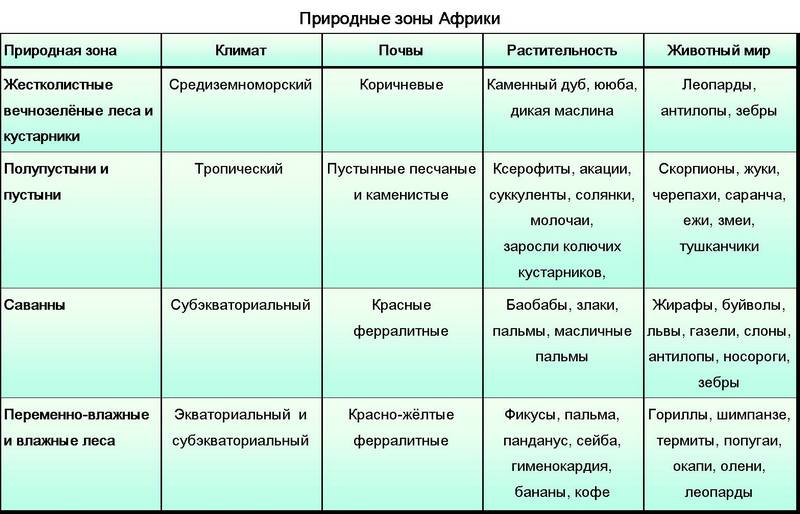
Natural areas of Africa, table
The main differences that characterize African natural areas:
- climate;
- soil;
- vegetation;
- animal world.
All these parameters are interconnected, because as a result of an established climate, certain soils are formed, on which only some plants grow. Vegetation becomes the basis of nutrition and habitat for representatives of the fauna. Based on the combination of all these indicators, the image of a particular zone is formed.
The table below of African natural zones gives a clear picture of all parts of the mainland.