Answers to paragraph 13
1. In which row are the formulas of only alkynes?
3)
2. Based on modern ideas about electron orbitals and their overlap, explain how chemical bonds are formed in an acetylene molecule and compare them with chemical bonds in an ethylene molecule. 
3. What hydrocarbon is the closest homologue of ethine?
propyne
4. How is acetylene obtained in the laboratory and in industry? Write the equations for the corresponding reactions. 
5. Propene and propyne can be detected with the same reagent
2) bromine water
6. The reaction product of propyne with an excess of bromine is
3) 1,1,2,2-tetrabromopropane
7. Where is acetylene used? Write the equations for the corresponding reactions.
Application of acetylene:
1) combustible when cutting and welding metals
2) starting material for the synthesis of vinyl chloride and various chlorine-containing solvents (tetrachloroethane, etc.)
8. Write the equations of chemical reactions that confirm the genetic relationship between the classes of organic compounds in Scheme 6. 
9. Make up the reaction equations with which you can carry out the following transformations. 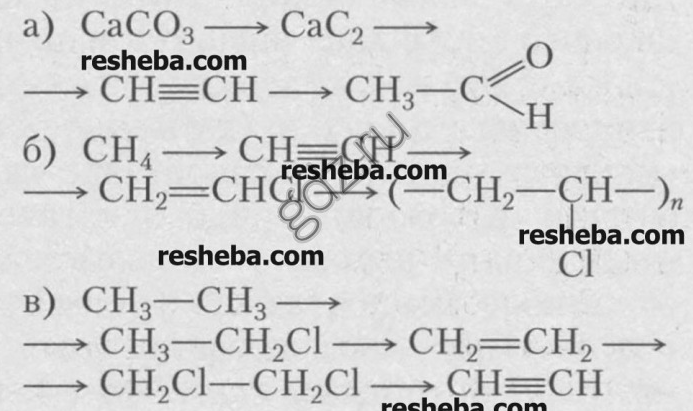
 Problem 1. The mass fraction of carbon in hydrocarbon is 0.8889. Its air density is 1.862. Find the molecular formula of this hydrocarbon, write the formulas and names of its possible isomers.
Problem 1. The mass fraction of carbon in hydrocarbon is 0.8889. Its air density is 1.862. Find the molecular formula of this hydrocarbon, write the formulas and names of its possible isomers. 
Task 2. What volume of acetylene (N.O.) can be obtained by reacting 51.2 kg of calcium carbide with water, if the mass fraction of the acetylene yield is 0.84 of the theoretical yield of the product? 
Problem 3. What volume of acetylene and what volume of hydrogen (n.o.s.) can be obtained from 1042 m3 of natural gas, the volume fraction of methane in which is 0.96? 
Task 4. What volume of air (n.o.s.) is required to burn 1 m3 of butyn-1?