Covalent bond: polar, non-polar, mechanisms of its appearance
The term “covalent bond” itself comes from two Latin words: “co” - jointly and “vales” - having power, since this is a bond that occurs due to a pair of electrons belonging to both at the same time (or, in simpler terms, a bond between atoms due to pairs of electrons that are common to them). The formation of a covalent bond occurs exclusively among the atoms of non-metals, and it can appear both in the atoms of molecules and crystals.
The covalent covalent was first discovered back in 1916 by the American chemist J. Lewis and for some time existed in the form of a hypothesis, an idea, only then it was confirmed experimentally. What did chemists find out about her? And the fact that the electronegativity of non-metals can be quite large and during the chemical interaction of two atoms the transfer of electrons from one to the other may be impossible, it is at this moment that the electrons of both atoms combine, a real covalent bond of atoms arises between them.
Types of covalent bond
In general, there are two types of covalent bond:
- exchange,
- donor-acceptor.
With the exchange type of a covalent bond between atoms, each of the connecting atoms represents one unpaired electron for the formation of an electronic bond. In this case, these electrons must have opposite charges (spins).
An example of such a covalent bond would be the bonds occurring in the hydrogen molecule. When hydrogen atoms approach each other, their electron clouds penetrate each other, in science this is called the overlap of electron clouds. As a consequence, the electron density between the nuclei increases, they themselves are attracted to each other, and the energy of the system decreases. However, when approaching too close, the nuclei begin to repel each other, and thus there is some optimal distance between them.
This is shown more clearly in the picture.
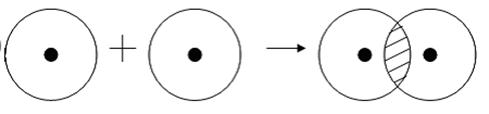
As for the donor-acceptor type of covalent bond, it occurs when one particle, in this case the donor, presents its electron pair for the bond, and the second, the acceptor, presents a free orbital.
Also, speaking about the types of covalent bonds, one can distinguish non-polar and polar covalent bonds, we will write about them in more detail below.
Covalent non-polar bond
The definition of a covalent non-polar bond is simple; it is a bond that forms between two identical atoms. An example of the formation of a non-polar covalent bond, see the diagram below.
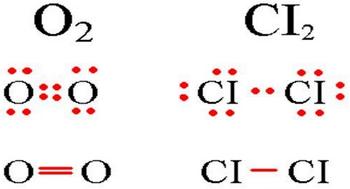
Diagram of a covalent non-polar bond.
In molecules with a covalent nonpolar bond, common electron pairs are located at equal distances from the nuclei of atoms. For example, in the oxygen molecule (in the diagram above), the atoms acquire an eight-electron configuration, while they share four pairs of electrons.
Substances with a covalent non-polar bond are usually gases, liquids, or relatively low-melting solids.
covalent polar bond
Now let's answer the question which bond is covalent polar. So, a covalent polar bond is formed when the covalently bonded atoms have different electronegativity, and the public electrons do not belong equally to two atoms. Most of the time, public electrons are closer to one atom than to another. An example of a covalent polar bond is the bond that occurs in a hydrogen chloride molecule, where the public electrons responsible for the formation of a covalent bond are located closer to the chlorine atom than hydrogen. And the thing is that chlorine has more electronegativity than hydrogen.

This is how a polar covalent bond looks like.
A striking example of a substance with a polar covalent bond is water.
How to determine a covalent bond
Well, now you know the answer to the question of how to define a covalent polar bond, and as non-polar, for this it is enough to know the properties and chemical formula of molecules, if this molecule consists of atoms of different elements, then the bond will be polar, if from one element, then non-polar . It is also important to remember that covalent bonds in general can only occur among non-metals, this is due to the very mechanism of covalent bonds described above.
Covalent bond, video
And at the end of the video lecture about the topic of our article, the covalent bond.